
Understand Reinstatement Value Policy (RVP) in insurance, how it differs from Market Value, benefits, claim conditions, and key points business owners must know.
What is Reinstatement Value Policy?
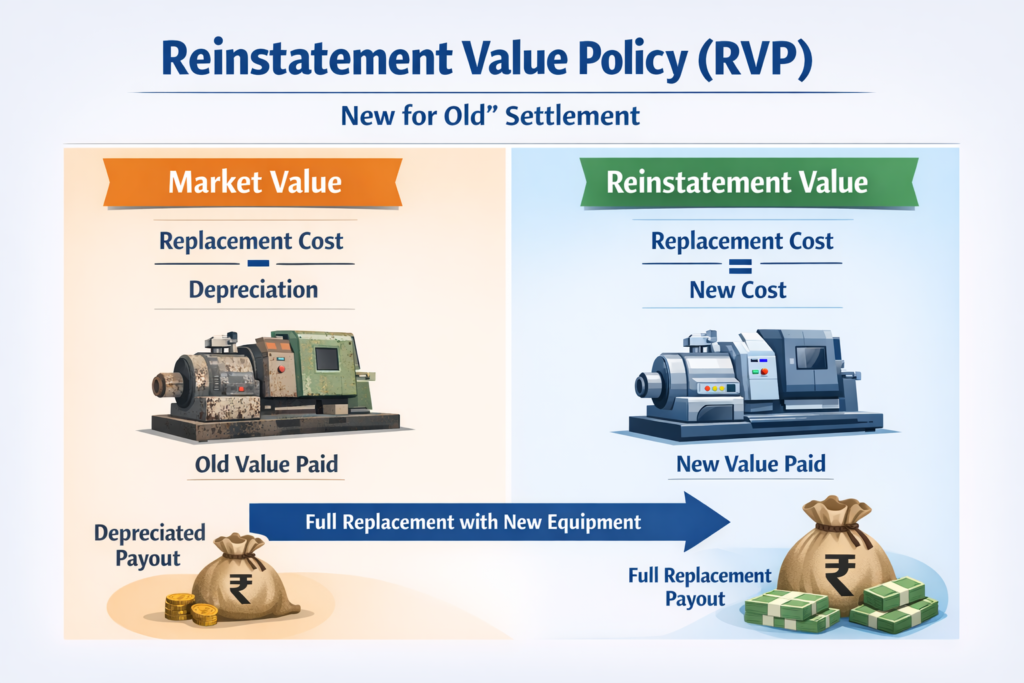
A Reinstatement Value Policy (RVP) is an insurance policy condition where damaged property is insured at the cost of reinstating or replacing it with a new item of the same kind, rather than paying only the depreciated value.
In simple terms, you get the cost of a new replacement, not the old item’s reduced value. This applies commonly to buildings, plant, machinery, furniture, and fixtures under Fire and Engineering insurance policies.
How Does a Reinstatement Value Policy Work?
Under a standard policy without reinstatement, claims are usually settled on Market Value (MV) — i.e., replacement cost minus depreciation. This can result in a lower payout.
Under RVP, the insurer pays the new replacement cost, subject to policy terms and adequate sum insured.
However, reinstatement is allowed only when:
- The property is insured for its new replacement value
- The property is actually reinstated or replaced
- Reinstatement happens within the stipulated time
- The reinstatement is similar to the original property
- The insured complies with policy conditions
If reinstatement is not carried out, the claim may revert to Market Value settlement.
Reinstatement Value vs Market Value — Key Difference
| Basis | Reinstatement Value Policy (RVP) | Market Value (MV) |
|---|---|---|
| Claim Settlement | New replacement cost | Depreciated cost |
| Depreciation Applied | No | Yes |
| Sum Insured Basis | New replacement cost | Current depreciated value |
| Typical Result | Higher payout | Lower payout |
| Common Use | Buildings, machinery | Older assets or MV policies |
Why Do Businesses Prefer Reinstatement Value Policy?
Many businesses select RVP because:
- Replacement of industrial machinery or buildings involves high capital cost
- Market Value settlement may leave large financial gaps
- Business continuity depends on timely reinstatement
- Assets depreciate on books but may still be in full use
- Banks and lenders often prefer RVP cover
RVP ensures that a loss does not create a financial burden due to depreciation.
When Does Reinstatement Apply?
Reinstatement generally applies to:
- Factory buildings
- Commercial buildings
- Machinery and plant
- Office equipment
- Furniture and fixtures
It typically does not apply to:
- Stock-in-trade
- Raw materials
- Consumables
- Obsolete or discarded machinery
These items are usually covered on Market Value basis.
How is the Sum Insured Decided Under RVP?
The Sum Insured must equal the full cost of replacing the property as new, including:
- Construction or purchase cost
- Installation/erection cost
- Freight and handling
- Duties and taxes (if applicable)
- Professional fees where relevant
If the sum insured is lower than the true reinstatement value, then underinsurance applies, and the claim payout may reduce proportionately.
Claim Settlement Under Reinstatement Value Policy — Simple Illustration
Assume:
- Replacement Cost of machinery (new): ₹50,00,000
- Current Market Value: ₹30,00,000
- Sum Insured under RVP: ₹50,00,000
- Loss assessed: Total loss
Under Market Value basis, settlement would be approx. ₹30,00,000 (depreciated value).
Under RVP, settlement is ₹50,00,000, subject to policy conditions and reinstatement.
If the sum insured was only ₹35,00,000, then underinsurance may apply — and the claim payout would reduce proportionately.
(This is only an illustrative explanation. Actual claims depend on full policy terms and circumstances.)
Important Conditions You Must Know
For RVP to apply correctly:
1. Reinstatement Must Be Done
Insurers expect the property to be reinstated or replaced. If not reinstated, the settlement may revert to Market Value.
2. Similar Property Must Be Used
Reinstatement should generally mean similar type, capacity, and usage. Significant upgrades or capacity changes may not be fully covered.
3. Time Limit Applies
Policies usually specify a time limit for reinstatement. Delays beyond the allowed period may affect settlement terms.
4. Adequate Sum Insured Is Essential
If the sum insured is lower than the actual replacement value, average clause (underinsurance) may apply.
Common Mistakes Made by Policyholders
Many insured parties unknowingly make errors such as:
- Using book value instead of new replacement cost
- Not revising sum insured after installing new machinery
- Ignoring taxes, freight, and erection costs
- Not updating schedules annually
- Underinsuring to reduce premium
- Assuming reinstatement applies to stock
These mistakes can reduce claim payout significantly.
Reinstatement Value Policy — Advantages
- Protects capital investments
- Ensures business continuity
- Reduces financial burden post-loss
- Aligns with modern replacement cost realities
Limitations to Keep in Mind
- Higher premiums due to higher sum insured
- Strict compliance with reinstatement timelines
- Underinsurance risk if values are not updated
- Not applicable to stock or consumables
Who Should Definitely Consider Reinstatement Value Policy?
RVP is particularly suitable for:
- Manufacturing units
- Processing plants
- Warehousing with fixed infrastructure
- Commercial offices
- Large residential complexes
- Institutions and industrial properties
Wherever fixed assets are critical for operations, reinstatement cover becomes important.
Best Practices to Manage Reinstatement Value Correctly
- Conduct regular insurance valuations
- Include all incidental and installation costs
- Update values after additions
- Maintain fixed asset registers
- Review policy terms annually
- Consult a professional when in doubt
This helps avoid disputes and ensures adequate protection.
Conclusion
A Reinstatement Value Policy ensures that insurance claims for buildings and machinery are settled on a new replacement cost basis, rather than depreciated value. This protects businesses from financial gaps, provided the sum insured reflects accurate replacement value, and policy conditions are fulfilled.
If you handle physical assets — whether industrial, commercial, or institutional — understanding reinstatement value is essential for proper risk protection and business continuity.















